The world is evolving at an unprecedented pace, and one generation that stands at the forefront of this transformation is the millennials. Born between 1981 and 1996, millennials are reshaping traditional norms and leaving an indelible mark on society, particularly in the realms of family formation and financial behavior. This article delves into the dynamics of millennial family choices, their impact on the economy, and how millennial women are driving a revolution in financial services.
Millennial Marriage Trends
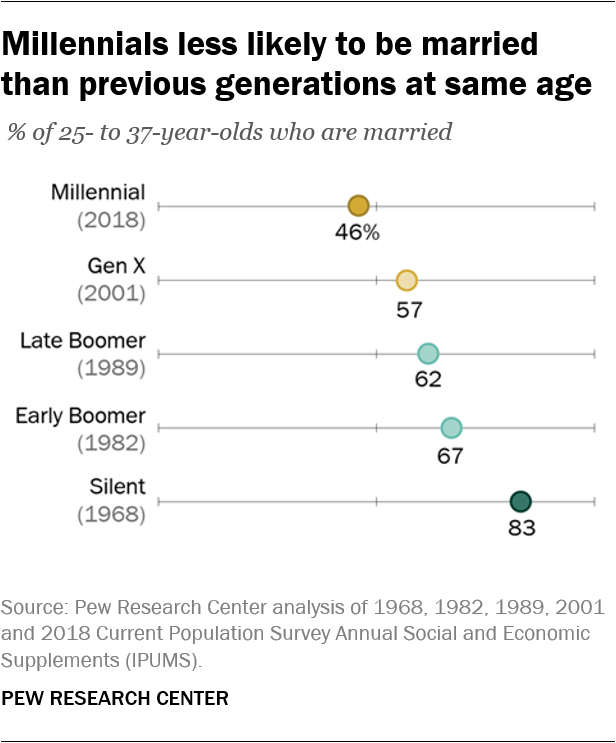
One of the most conspicuous shifts in millennial behavior is their approach to marriage. Unlike their predecessors, millennials are choosing to delay marriage for various reasons. Economic considerations play a role in this decision-making process. Many millennials are saddled with student loan debt, and the scars of the Great Recession have made them more cautious. Financial stability often takes precedence over wedding vows.
However, it’s not just economic factors at play. Millennials are also influenced by changing societal norms. The emphasis on individuality, personal growth, and the desire for more meaningful relationships have led them to rethink the timing of marriage. Cohabitation and parenthood outside of wedlock have become more accepted, redefining traditional family structures.
Notably, between 2019 and 2021, there was a significant surge in household growth, largely driven by millennials. This boost in household formation was due to an increase in the headship rate, which measures the share of the population heading their own households. Headship rates rose across all age groups, but the most significant increases occurred among those aged 25-34 and 35-44, which were also the ages with the most declines earlier in the decade. In 2011-2016, falling headship rates dampened household growth by 579,000 per year below the average levels that growth in the adult population alone would have generated. The opposite happened in 2016-2021, where rising headship rates resulted in 640,000 of the 1.7 million average annual household growth.2 This surge was influenced by factors like rising wages, stimulus payments, and a pause in student loan payments, resulting in a substantial increase in household formation. It appears that older millennials are finally establishing the households that were postponed in the earlier part of the decade.
Fertility Patterns Among Millennials
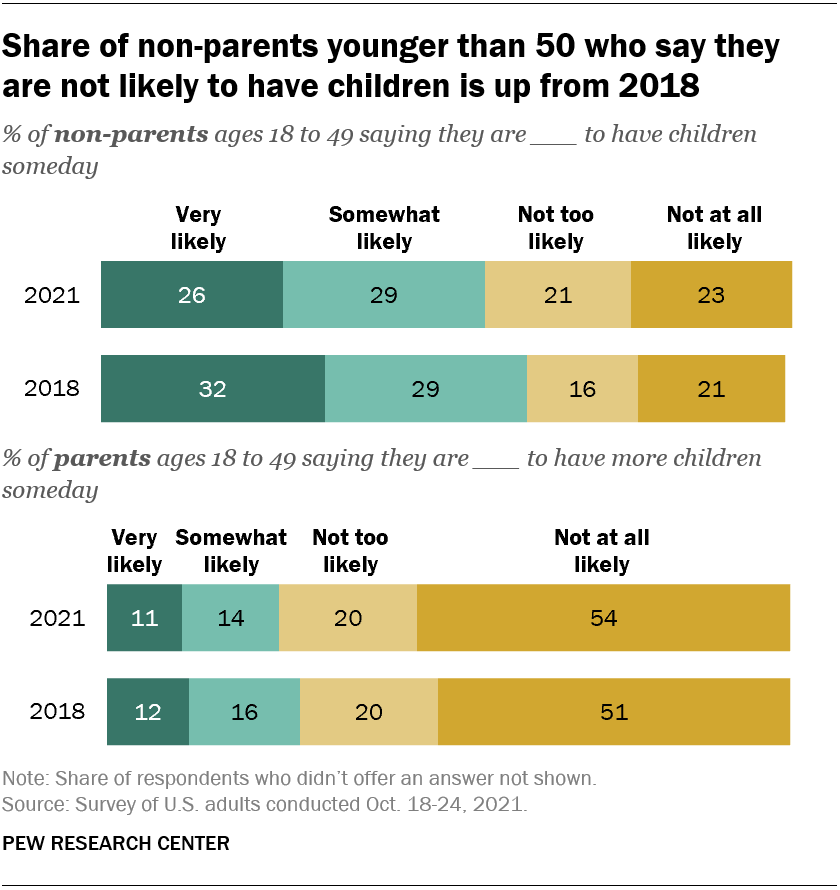
In addition to changing marriage trends, millennials are transforming the landscape of family planning. The age at which millennials are having children has increased, and they are opting to have fewer children than previous generations.3 The reasons behind this shift are multifaceted.
Economic realities are a significant factor. The financial strain of the Great Recession, coupled with soaring housing costs and the burden of student loan debt, has led millennials to take a more cautious approach to expanding their families. Income dynamics, rising childcare costs, and shifting priorities influence Millennials’ fertility rates. As they delay parenthood, they have fewer children later in life, resulting in a decline in birth rates.
Women’s Economic Impact
A standout feature of the millennial generation is the educational attainment of its women. Millennials boast the highest levels of education in history, with 39% holding at least a bachelor’s degree.4 This surge in educational achievement has empowered millennial women.
One of the most noteworthy outcomes is the narrowing of the gender pay gap. Millennial women earn 89% of what their male counterparts earn, a gap that continues to close steadily.4 In many millennial households, women have assumed the role of primary earners, financial decision-makers, and investment decision-makers. This shift is challenging traditional gender roles and reshaping economic dynamics within families.
Changing Financial Behavior
Millennials are not just redefining family structures; they are also evolving in their financial behavior. They save a remarkable 36% more of their annual salaries compared to previous generations4. Moreover, millennials are displaying a greater appetite for risk, with a significant portion of their portfolios allocated to equities—a marked departure from the conservative investment strategies of previous generations.
Perhaps most intriguing is their financial priorities. Retirement planning has become a paramount concern. Millennials have also shown an interest in investing with a focus on ESG (environmental, social, and governance) impact.4 Millennials are driven by a desire to align their investments with their values, signaling a profound shift in the financial services landscape.
Market and Financial Services Impact
The impact of millennials on the economy is expected to be profound. Their higher savings rates and preference for equities are poised to influence future market dynamics. As they become the largest demographic group in the U.S. economy, understanding their values and behaviors is paramount for assessing opportunities and risks across various sectors.
Additionally, millennial women are taking the lead in reshaping the financial services industry. Their increasing influence in investment decisions represents a significant departure from the male-dominated landscape of the past. They tend to conduct more research, adopt long-term perspectives, and trade less frequently—factors that can have a substantial impact on investment outcomes.4
Conclusion
In conclusion, millennials are not only redefining family dynamics and financial behavior but are also driving a transformative wave across various sectors of the economy. As they continue to shape the new economic era, businesses, and financial institutions must adapt to meet their evolving needs and preferences. Flexibility, innovation, and a deep understanding of millennial values and behaviors are key to thriving in this new economic landscape. The millennials are here, and their influence is only set to grow stronger with time.
Written by: Linda Wang
References:
- “Millennial life: How young adulthood today compares with prior generations.” Pew Research Center, Washington, D.C. (February 14, 2019) How Millennials compare with prior generations | Pew Research Center
- The Surge in Household Growth and What It Suggests About the Future of Housing Demand | Joint Center for Housing Studies (harvard.edu)
- “Growing share of childless adults in U.S. don’t expect to ever have children.” Pew Research Center, Washington, D.C. (November 19, 2021) More childless U.S. adults now say they don’t plan to ever have kids| Pew Research Center
- This is how millennials are shaping the new economy (cnbc.com)